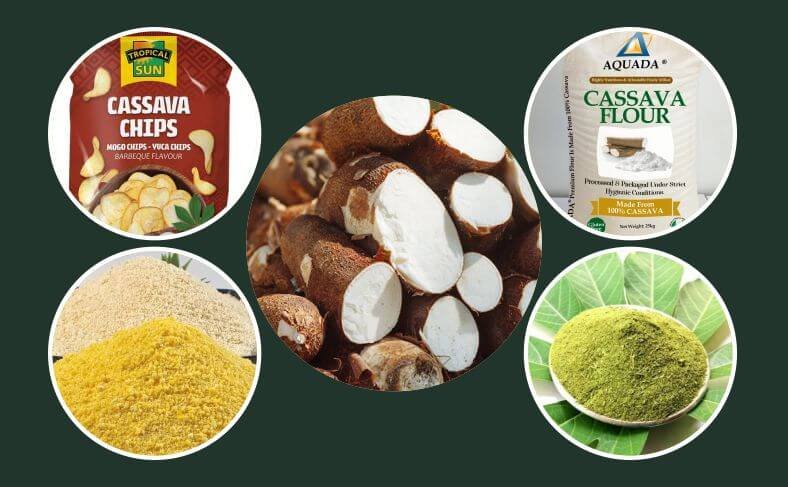
The cassava value chain extends far beyond the root, with a wide range of cassava products derived from every part of the plant. Discover how these byproducts are transforming industries globally.
The Cassava plant isn’t just about carbs and food, it’s a source of numerous byproducts used in various industries.
From biofuels to animal feed, cassava products are making a real difference in areas like food security, sustainability, and even health.
This plant produces more than just edible products; it’s an essential resource for creating materials, industrial products, and even medicines.
With cassava’s many applications, industries are discovering innovative ways to tackle challenges such as renewable energy and nutrition.
In this guide, we’ll introduce you to 47 cassava byproducts, highlighting their diverse uses and the role they play in markets worldwide.
Get ready to learn how this unassuming plant is used far beyond the kitchen and how its byproducts are contributing to various industries.
What are Cassava Products?
Cassava products are products from different parts of the cassava plant, including the root and stem. They include garri cassava flakes, flour, animal feed, starch, ethanol, biofuel, fufu, and adhesives.
The most common product is cassava flour, used in gluten-free baking and cooking.
Tapioca pearls, often found in bubble tea, and tapioca starch, used as a thickener in sauces and soups, are also popular.
Cassava chips, similar to potato chips, are a crunchy snack made from sliced and fried cassava.
Industrially, cassava is processed into biofuels, animal feed, and even textiles. Its versatility makes it a key crop in food industries and sustainable manufacturing.
Related: The Place of Cassava Root in Global Market
List of Products Made from Cassava
Let’s take a look at some of the key products along the cassava value chain.
1. Cassava peel
The cassava peel is one of the byproducts of cassava used in producing other cassava products, like feeds. It is the outer skin of the cassava root that is discarded by traditional cassava processors.
Cassava peels can be very useful in animal feed because of its high content of fiber. It is also used as a source of fuel for biofuel feedstock and a substrate for biogas production.
And we also believe that the research being carried out along the cassava value chain will find more uses of the cassava peels.
2. Cassava leaves

Cassava leaf is another cassava product that is stunningly beneficial both for humans and animals.
In my cassava-farming community, we never tried to eat cassava leaves because of ignorance, but as knowledge about the plant increased, we knew better.
The cassava leaves are a very nutritious part of the cassava plant that is given less attention.
The yuca leaves are protein-rich and packed with important vitamins and minerals, with needed health benefits.
They are used in traditional dishes as vegetables and can also be processed into powder for cosmetics and supplements.
Certainly, manioc leaves have health benefits and can be further researched to be able to exploit their nutritional and cosmetic benefits.
3. Cassava pulp
Cassava pulp, of course, is the fibrous residue of the cassava root from local traditional processing of the root.
We discarded them because they are so fibrous that they can’t cook when joined with other parts of the root in cooking, and so are left for the local birds and animals.
However, with further understanding, these pulps are good for animal feed, biofuel feedstock, and also a good source of organic matter for compost.
By channeling cassava pulp to these areas, we can use what we thought was waste for proper use.
4. Cassava starch
Cassava starch, also known as tapioca, a key product of cassava processing, has a wide range of industrial applications.
In Nigeria, there is a popular tribal delicacy based on cassava starch, and a delight to people who have it for the first time.
This is after the starch has undergone some local processes.
As one of the foremost cassava products, cassava starch can be used in the production of cassava packages, food production, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and even as a binding agent in paper production.
When we explore more cassava starch, we can reduce the pressure mounted on the starch obtained from corn and other sources.
5. Cassava flour

Cassava or manioc flour is the chief and most popular cassava product that modern cassava processing targets.
In recent times, it has been in high demand because of its gluten-free status.
As one of the cassava products, starch from cassava is used in baking, cooking, and as a thickener in sauces and soups.
Another importance of cassava flour is its digestive attributes because of its resistant starch, and it also helps to regulate blood sugar.
Incorporating yuca flour into diets can improve our health and also impact cassava farmers economically.
6. Cassava chips

Cassava chips is one of the popular cassava products. Cassava chips come in two types.
The fried cassava chips and the dried cassava chips.
Fried chips are the ones prepared to be eaten while the dried ones are dried to preserve them for further processes into animal feeds or other purposes.
Among other cassava-based foods, cassava chips are a common product derived from the cassava root.
The dried cassava chips are made by cleaning, chipping, and sun-drying the cassava roots for 3-6 days.
This process reduces the cyanide content to safe levels. Cassava chips are a source of carbohydrates and are used as animal feed.
Also, the cassava root serves as a snack and is a better option than potato chips as it contains less acrylamide, a suspected carcinogen.
Related: Tools and Equipment for Cassava Processing
7. Cassava pellets
Cassava pellets are compact, cylindrical cassava products made from cassava roots and stems, used as a source of energy in animal feed.
They have a lower nutritional value than chips due to the inclusion of shoot parts, which increase fiber and ash content.
Both products are widely used in various industries, including animal feed, distilleries, and pharmaceuticals.
8. Cassava ethanol
Cassava ethanol is produced by fermenting cassava starch or molasses and distilling it into alcohol.
As a cassava product, cassava ethanol is used as a biofuel for vehicles or as a cleaner alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
Production of more cassava ethanol reduces greenhouse gas emissions and supports sustainable energy solutions.
9. Cassava biofuel
Cassava biofuel is a product of cassava starch through fermentation and distillation processes.
It is a renewable energy source used to power vehicles, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating environmental pollution.
Cassava biofuel is energy-efficient, with a high energy output-to-input ratio, making it a promising alternative to traditional fuels.
10. Cassava animal feed
As mentioned above, cassava by-products such as peel, pulp, and leaves can be used as animal feed for livestock such as pigs, cows, and poultry.
The cassava-based animal feed provides a cost-effective and nutritious alternative to traditional feed sources, helping farmers improve their livestock’s health and productivity.
11. Cassava glue/adhesive
Cassava starch can also be used as a raw material for producing glue or adhesive products.
Cassava-based glue is non-toxic, biodegradable, and cost-effective, making it a suitable alternative to synthetic adhesives in various industries.
12. Garri

Garri is a popular edible food in West Africa, particularly in Nigeria. As the most popular cassava product in Nigeria, it is the cheapest and most eaten staple in the country.
It is produced from cassava tubers and involves several steps: washing and peeling, crushing, fermentation, dewatering, and frying.
Garri can be consumed directly or used as an ingredient in various dishes.
It is often mixed with water, sugar, or other ingredients and can be stored for long periods.
13. Akpu/Fufu
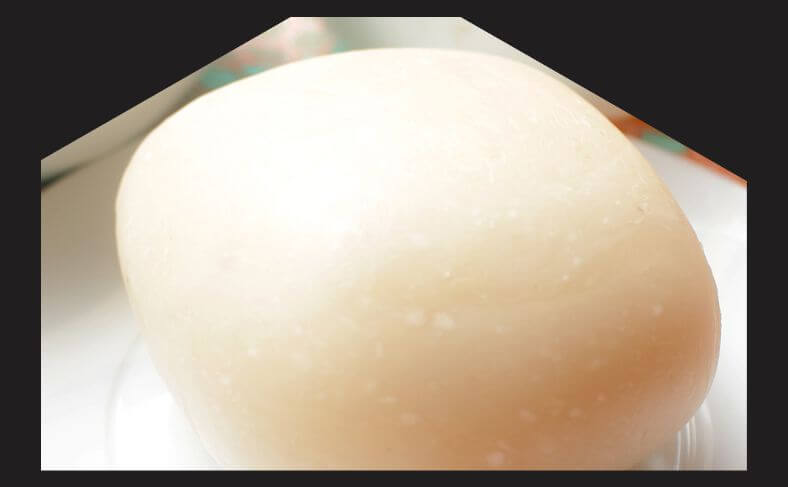
Akpu, also known as fufu, is a traditional West African food made from fermented cassava.
To make akpu, cassava roots are peeled, soaked in water for several days to ferment, and then mashed or pounded into a smooth, dough-like consistency.
The resulting paste is typically boiled or steamed until firm. Akpu is a staple food in Nigeria and other parts of West Africa, where it is enjoyed alongside soups and stews.
14. Tapioca
Tapioca is a product derived from the starch of cassava roots.
After cassava is harvested, its roots are processed to extract the starch, which is then dried and formed into various products like tapioca pearls, flakes, or flour.
Tapioca pearls, commonly used in bubble tea, have a chewy texture, while tapioca flour serves as a gluten-free thickening agent for soups, sauces, and baked goods.
It’s prized for its neutral flavor, making it adaptable to both sweet and savory dishes. Tapioca is a staple in many global cuisines, particularly in South America, Africa, and Asia.
15. Abacha

Abacha, also known as African salad, is a traditional Nigerian dish made from cassava.
To prepare abacha, cassava tubers are peeled, boiled, and then shredded into thin strips.
These strips are sun-dried until they become crispy and can be stored for later use.
When ready to serve, the dried cassava is soaked in water to soften, then mixed with palm oil, spices, vegetables, and sometimes fish or meat.
Abacha is a popular delicacy in southeastern Nigeria, enjoyed as a light meal or snack, appreciated for its unique texture and combination of flavors.
16. Cassava Flour Tortillas
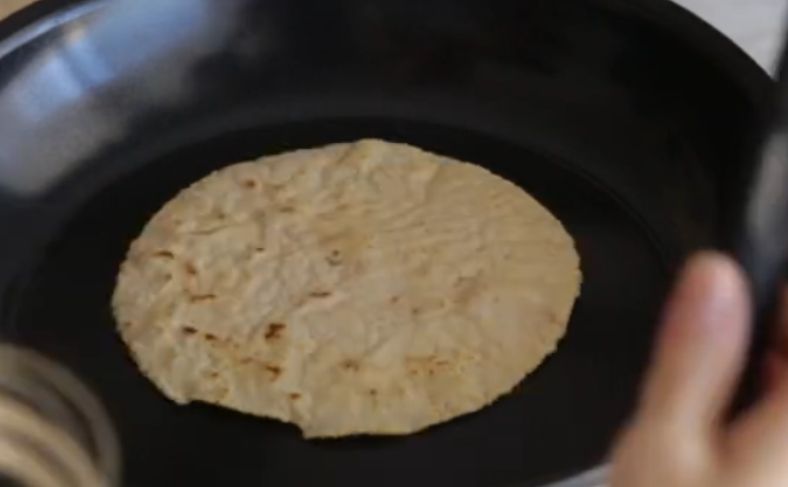

Cassava tortillas are a gluten-free alternative to traditional corn or wheat tortillas, made from cassava flour.
The flour, derived from the starchy roots of cassava, is mixed with water, oil, and salt to create a dough, which is then rolled out and cooked on a hot surface.
Cassava tortillas have a soft, pliable texture and a slightly earthy flavor, making them perfect for tacos, wraps, or other flatbread uses.
They are a popular cassava product among those seeking grain-free or gluten-free options and are valued for their versatility and ability to hold up well to various fillings and toppings.
17. Tapioca Pearls
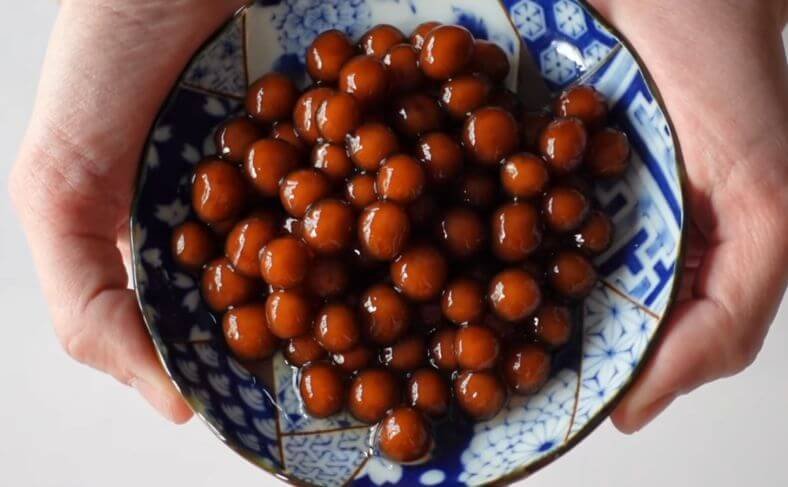

Tapioca pearls are among the foremost cassava products. They are small balls made from tapioca starch, which is derived from the cassava root.
They are commonly used in desserts and beverages, most famously in bubble tea.
To create tapioca pearls, tapioca starch is mixed with water to form a dough, which is then shaped into small balls and cooked.
When cooked, they become translucent and have a slightly sweet flavor.
18. Cassava Pie
Cassava pie is a delicious baked dish made primarily from cassava flour and grated cassava.
The base is often prepared by mixing grated cassava with eggs, milk, and sugar, resulting in a sweet, custard-like filling.
The mixture is poured into a pie crust and baked until golden and set. This dessert showcases the unique texture and flavor of cassava, which adds a subtle nuttiness to the pie.
Cassava pie is popular in various regions, particularly in South America and the Caribbean, where it is often served at festive occasions and gatherings. See a dedicated post on cassava pie here.
19. Cassava Muffins
Cassava muffins are a gluten-free alternative made from cassava flour, offering a light and fluffy texture.
The batter combines cassava flour with ingredients like eggs, milk, sugar, and baking powder, resulting in a versatile treat.
These muffins can be sweetened with fruits, nuts, or spices, making them suitable for breakfast, snacks, or dessert.
Their natural sweetness and moisture make them appealing to those with dietary restrictions, and they can be enjoyed fresh or toasted.
Cassava muffins are popular in various cultures, highlighting cassava’s adaptability in baked goods.
20. Cassava Bread
Cassava bread is a traditional staple made from cassava flour, widely enjoyed in many tropical regions.
The dough is prepared by mixing cassava flour with water and sometimes eggs or milk, then kneading until smooth.
It is shaped into flatbreads and baked, resulting in a chewy texture and slightly nutty flavor.
Cassava bread serves as an excellent gluten-free option for sandwiches or as an accompaniment to soups and stews.
In some cultures, it holds significant cultural importance and is often used in festive meals, showcasing cassava’s versatility in various culinary traditions.
21. Yuca Fries

Yuca fries, also known as cassava fries, are a popular snack or side dish made from the starchy roots of cassava.
To prepare yuca fries, the cassava roots are peeled, boiled until tender, and then cut into strips or wedges.
They are typically deep-fried or baked until crispy and golden. Yuca fries have a crunchy exterior and a soft, fluffy interior, making them a delightful alternative to traditional potato fries.
Often served with dipping sauces, they are enjoyed in various cuisines, particularly in Latin America and the Caribbean, where they are a beloved comfort food.
22. Cassava Pancake
Cassava pancakes are gluten-free breakfast cassava products made from cassava flour or grated cassava.
The batter typically combines cassava with eggs, milk, and a leavening agent, resulting in a smooth and pourable mixture.
These pancakes can be cooked on a griddle until golden brown, creating a soft, fluffy texture. Cassava pancakes have a mild flavor that pairs well with sweet or savory toppings, such as maple syrup, honey, or fresh fruit.
They are popular in various cultures, offering a nutritious alternative to traditional pancakes while showcasing the versatility of cassava in breakfast dishes.
23. Cassava Cake
Cassava cake is a popular dessert in many tropical regions, particularly in the Caribbean and Southeast Asia.
Made from grated cassava, coconut milk, sugar, and eggs, the cake is baked until it has a firm, moist texture.
The natural sweetness of cassava combined with the creaminess of coconut milk creates a rich flavor profile.
Often topped with grated coconut or a layer of cheese, cassava cake is enjoyed as a festive treat during celebrations and gatherings.
Its unique taste and texture make it a favorite among those seeking gluten-free dessert options. See an in-depth post on cassava cake.
24. Cassava Biscuits
Cassava biscuits are a gluten-free snack or treat made primarily from cassava flour.
The dough is typically prepared by combining cassava flour with butter, sugar, and baking powder, resulting in a crumbly, tender texture.
These biscuits can be flavored with various ingredients, such as herbs, spices, or cheese, making them versatile for both sweet and savory options.
Cassava biscuits are often enjoyed with tea or coffee and can be served as a light snack or appetizer.
Their unique texture and flavor highlight the adaptability of cassava in baked goods.
25. Cassava Pudding
Cassava pudding is a delightful dessert made from grated cassava, coconut milk, sugar, and spices like nutmeg or vanilla.
The mixture is baked until it sets into a smooth, creamy texture with a slight chewiness from the cassava.
This pudding is popular in many Caribbean and tropical regions, often served at family gatherings and celebrations.
The natural sweetness of cassava combined with the richness of coconut milk creates a comforting dessert that is both satisfying and flavorful.
Cassava pudding is enjoyed warm or chilled, showcasing the versatility of cassava in sweet dishes.
26. Cassava Syrup
Cassava syrup, one of the obscure cassava products, is a sweet liquid derived from cassava roots through the extraction and conversion of starch.
Known for its mild, neutral flavor, this syrup is used as a healthier alternative to traditional sweeteners like sugar and high-fructose corn syrup.
It’s commonly used in beverages, baked goods, and snacks.
Cassava syrup is particularly popular in low-carb, gluten-free, and paleo diets due to its natural composition and relatively low glycemic index.
It also serves as a more sustainable, plant-based sweetening option, with increasing demand in natural food markets.
27. Cassava Starch Paper
Cassava starch paper is an eco-friendly alternative to traditional paper products.
Made by processing cassava starch, this biodegradable paper offers a sustainable option for packaging and disposable products like plates, cups, and wrappers.
It decomposes faster than conventional paper, reducing its environmental impact.
Cassava starch paper is gaining traction in industries looking to reduce waste and promote green alternatives.
It’s a vital component in the move towards sustainable packaging solutions, especially in foodservice, where it is used as a renewable substitute for plastic and Styrofoam products.
28. Cassava Vinegar
Cassava vinegar is a fermented product made from the starch of cassava roots, offering a mild, slightly sweet taste.
Produced through fermentation, this vinegar is used in cooking, particularly for salad dressings, marinades, and sauces.
With its natural probiotic content, cassava vinegar is becoming a popular alternative to traditional vinegar types, offering both culinary and health benefits.
It is prized for its unique flavor profile and is often marketed as a natural and less acidic option compared to other vinegars.
Its probiotic properties may aid digestion and support gut health.
29. Cassava Protein (for food supplements)
Cassava protein is a plant-based protein extracted from cassava roots, commonly used in food supplements. See cassava supplements.
Ideal for those on vegan, gluten-free, or allergen-free diets, cassava protein is a nutritious alternative to animal-derived proteins.
It is rich in essential amino acids, providing the body with vital building blocks for muscle growth, energy production, and overall health.
Sustainable and environmentally friendly, cassava protein serves as a great option for supporting muscle health and aiding digestion.
It’s increasingly found in protein powders, smoothies, and other dietary supplements.
30. Cassava Tea
Cassava tea is a light, herbal beverage made from the leaves and stems of the cassava plant.
Often consumed as a caffeine-free alternative to traditional teas, cassava tea is believed to offer a variety of health benefits, including improved digestion, immune support, and hydration.
Rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients, this tea is a popular choice for those seeking natural remedies.
It’s especially valued for its gentle, mild flavor and ability to support overall health, making it a refreshing and nourishing drink for daily consumption.
31. Cassava-based Pasta
Cassava-based pasta is a gluten-free alternative to traditional wheat pasta, made from cassava flour.
This type of pasta offers a similar texture and flavor to regular pasta, making it a popular option for individuals with celiac disease or those following gluten-free or low-carb diets.
Cassava pasta can be used in various dishes, from Italian pasta recipes to Asian-inspired stir-fries.
It is easy to prepare and digest, providing a healthy, plant-based substitute for wheat-based pasta that is both satisfying and nutritious.
32. Cassava-based Noodles
Cassava-based noodles are another gluten-free, grain-free option for those who love noodles.
Made from cassava flour, these noodles provide a chewy, satisfying texture similar to traditional wheat noodles.
They are commonly used in Asian and Mediterranean dishes such as stir-fries, soups, and salads.
Cassava noodles are an excellent option for those with dietary restrictions, including individuals with gluten sensitivity or those following low-carb diets.
Versatile and easy to cook, they are a healthy alternative that maintains flavor and texture in various noodle-based recipes.
33. Cassava Oil
Cassava oil is a cooking oil derived from the roots of the cassava plant. With a high smoke point, it is ideal for frying and sautéing.
The oil is rich in essential fatty acids, making it a nutritious choice for culinary uses.
In addition to its culinary applications, cassava oil is increasingly used in cosmetics and personal care products due to its moisturizing and nourishing properties.
It is known for its skin-softening qualities and is commonly found in lotions, creams, and hair care products.
It offers a versatile, healthy fat alternative for various uses.
34. Cassava-based Snacks
Cassava-based snacks are made from cassava flour or chips, providing a crunchy, gluten-free alternative to traditional potato-based snacks.
These snacks are low in fat and can be flavored with a variety of seasonings, offering a satisfying option for health-conscious consumers.
Cassava-based snacks are particularly popular in plant-based and low-carb diets, as they provide a nutritious, fiber-rich alternative.
Whether in the form of chips, crackers, or bars, these snacks offer a delicious, wholesome option for those seeking gluten-free or allergen-free snack alternatives.
35. Cassava Soup
Cassava soup is a savory dish made from cassava tubers, often combined with vegetables, meats, or fish.
A staple in many African and Caribbean cuisines, this soup is known for its hearty and comforting texture.
Cassava is a good source of carbohydrates, providing long-lasting energy.
The soup is both filling and nutritious, offering a rich blend of flavors and essential nutrients.
It’s perfect for cool weather or as a filling meal, often accompanied by spices and seasonings that enhance its flavor and aroma.
36. Cassava Porridge
Cassava porridge is a comforting, creamy dish made by cooking grated cassava with water or milk.
Often enjoyed as a breakfast or snack, it can be sweetened with sugar, honey, or milk, or prepared savory with salt and spices.
Rich in carbohydrates, cassava porridge provides a quick source of energy and keeps you feeling full for longer.
Popular in many cultures, this nutritious porridge is versatile, allowing for various flavor combinations and can be enjoyed hot or cold, making it a satisfying, hearty meal.
37. Cassava Ice Cream
Cassava ice cream is a dairy-free, gluten-free frozen dessert made from cassava flour or starch.
Offering a smooth, creamy texture similar to traditional ice cream, it can be flavored with a variety of ingredients like fruits, chocolate, or nuts.
This frozen treat is an ideal choice for those following vegan, gluten-free, or low-carb diets, providing a guilt-free indulgence.
Cassava ice cream offers a versatile dessert option that caters to different dietary needs, making it a popular alternative to conventional ice cream.
38. Cassava Juice
Cassava juice is made by extracting the liquid from cassava roots, offering a refreshing and nutrient-rich beverage.
Known for its mild, slightly sweet flavor, cassava juice is popular in various cultures and is often consumed as a detoxifying or energy-boosting drink.
Packed with natural carbohydrates, this hydrating beverage helps provide a quick energy boost.
It can be enjoyed on its own or flavored with additional fruits and spices, making it a delicious and nutritious refreshment, particularly in tropical regions.
39. Cassava-based Cookies
Cassava-based cookies are gluten-free treats made from cassava flour, offering a chewy, delicious texture.
These cookies can be customized with a variety of flavorings, such as chocolate chips, nuts, or dried fruits, catering to different tastes and dietary preferences.
Perfect for those with gluten intolerance or following low-carb diets, cassava-based cookies provide a healthier alternative to traditional cookies.
Rich in fiber and free from common allergens like wheat, these cookies are an excellent choice for a tasty, guilt-free snack or dessert.
40. Cassava Tapioca Flour
Cassava tapioca flour, also known as tapioca starch, is derived from the cassava root and is a staple in gluten-free baking and cooking.
Its neutral flavor and thickening properties make it ideal for creating sauces, soups, desserts, and gluten-free baked goods.
Cassava flour is known for providing smooth textures and elasticity in recipes, making it a popular choice in various cuisines.
It’s often used in combination with other gluten-free flours, helping create baked goods with a familiar texture that mimics traditional wheat flour-based recipes.
41. Cassava-based Crackers
Cassava-based crackers are gluten-free, crunchy snacks made from cassava flour. They include:
These light, crispy crackers can be flavored with a range of herbs, spices, or seeds, making them a versatile and satisfying treat.
Perfect for individuals with gluten intolerance or those following a low-carb or keto diet, cassava crackers offer a healthier snack alternative.
Rich in fiber and free from common allergens, these crackers are ideal for serving with dips, cheese, or as a stand-alone snack, making them a delicious, guilt-free option for health-conscious consumers.
42. Cassava-based Cake Mixes
Cassava-based cake mixes are convenient, pre-packaged options made with cassava flour, offering a gluten-free alternative to traditional cake recipes.
These mixes make baking gluten-free cakes easy and hassle-free, perfect for those with dietary restrictions.
Cassava-based cake mixes can be customized with fruits, nuts, or frosting, allowing for a variety of flavor combinations.
These mixes provide a simple solution for making cakes that are both delicious and suitable for those avoiding gluten, making them a popular choice for anyone looking to indulge in a gluten-free dessert.
43. Cassava Polenta
Cassava polenta is made from finely ground cassava flour and serves as a gluten-free alternative to traditional cornmeal-based polenta.
This dish offers a smooth, creamy texture when cooked and can be served as a side dish or main course.
Cassava polenta is versatile and can be flavored with herbs, cheeses, or spices, offering a comforting and hearty meal.
It’s a great choice for those following gluten-free, low-carb, or paleo diets, providing a nutritious, filling meal with a flavor profile similar to traditional polenta.
44. Cassava-based Pizza Crust
Cassava-based pizza crust is a gluten-free, grain-free alternative to traditional pizza dough.
Made from cassava flour, this crust offers a chewy, crispy texture, making it a popular choice for individuals with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease.
It’s perfect for those following a low-carb or gluten-free diet who still want to enjoy pizza.
The cassava-based crust can be topped with a variety of ingredients, from classic cheese and tomato to unique vegetables and meats, offering a delicious, nutritious option for pizza lovers with dietary restrictions.
45. Cassava Wafers
Cassava wafers are thin, crunchy snacks made from cassava flour, offering a gluten-free alternative to traditional potato chips or crackers.
Often lightly salted or flavored with herbs and spices, these wafers provide a satisfying snack option that is low in carbs and free from gluten.
Ideal for health-conscious individuals or those with gluten intolerance, cassava wafers are a delicious, light snack that can be enjoyed on their own or paired with dips.
They offer a healthier, guilt-free option for those looking to indulge without compromising on nutrition.
46. Cassava Gel (used in cosmetics)
Cassava gel is derived from cassava starch and is widely used in cosmetics and skincare products.
Known for its moisturizing and thickening properties, it’s a natural, gentle ingredient found in lotions, creams, and shampoos.
Cassava gel helps hydrate the skin, leaving it feeling soft and smooth without the use of harsh chemicals.
It is commonly used in personal care products for its ability to soothe and nourish the skin, making it a popular choice in natural beauty products aimed at promoting healthy, hydrated skin.
FAQS on Cassava Products
What are the 5 products of cassava?
- Cassava flour
- Cassava starch
- Garri
- Cassava chips
- Fufu
What are 10 things made from cassava?
- Bread
- Cakes
- Biscuits
- Pastry
- Cookies
- Candy
- Pasta
- Couscous
- Starch-based products
- Biodegradable plastics
What can cassava be processed into?
- Starch
- Flour
- Garri
- Chips
- Animal feed
- Food products
- Industrial products
- Bio-degradable products
- Glucose
- Fructose
- Modified starches
What is cassava made?
Cassava is made from the roots of the cassava plant, which are high in starch and can be processed into various products, such as those mentioned above.
Final Word from Cassava Pathway
The cassava value chain illustrates the immense potential of a single crop to power food systems, industrial applications, and economic resilience.
Cassava-based foods around the world, like garri, fufu, flour, and tapioca, are dietary staples in many regions and are expanding globally due to their health benefits and culinary versatility.
Beyond edibility, cassava peels, pulp, and leaves serve in sustainable animal feed production, while cassava starch is foundational in glue, textiles, and biofuel industries.
As global interest grows in climate-resilient and economically viable crops, cassava stands out not only for its agricultural productivity but for its wide-ranging uses.
Embracing and innovating across the cassava value chain will help solve pressing challenges in nutrition, sustainability, and economic development, making cassava-based products essential now and in the future.
Citations:
- Cassava processing chains in Africa
- Cassava products in Nigeria
- Cassava utilization for noodle production
- Cassava Flour and Starch: Processing Technology and Utilization
- Nine Uses and Industry Applications of Cassava Starch

Chimeremeze Emeh is a writer and researcher passionate about Africa’s most transformative root crop—cassava. Through his work at cassavavaluechain.com, he explores the entire cassava industry, from cultivation and processing to its diverse applications in food, health, and industrial use.
He also writes for palmoilpalm.com, where he shares his extensive experience and deep-rooted knowledge of palm oil, covering red palm oil, palm kernel oil, and refined products. His work there reflects his lifelong connection to agriculture and his commitment to promoting sustainable value chains in Africa.
Driven by curiosity and purpose, Chimeremeze aims to shed light on how cassava continues to empower communities, strengthen food systems, and link traditional farming wisdom with modern innovation.

